The concept of the customer journey map in the era of connectivity (the era in which customers are connected to the Internet) advocated in Marketing 4.0 has changed significantly from the traditional approach of the era in which Internet connectivity was not taken into account.
The customer journey in the AIDMA and 4A concepts was shaped like a funnel, in which the number of targeted people was reduced as the process from awareness to action narrowed down. In recent years, however, the funnel (=funnel) shape has evolved into a double funnel shape, where what is squeezed expands again by being shared rather than squeezed out. And with the 5A customer journey, instead of the idea of a funnel, the structure was designed to allow customers to enter from anywhere in the customer journey.

Contents
- 0.1 Funnel-shaped model not affected by the Internet
- 0.2 Models that take into account online sharing and diffusion
- 0.3 How the 5A customer journey has changed
- 0.4 Processes and customer touch points of AWARE、APPEAL、ASK、ACT、ADVOCATE
- 1 5A customer journey, to aim all people who are aware of the brand will advocate it.
Funnel-shaped model not affected by the Internet
AIDMA customer journey
①Attention→②Interest→③Desire→④Memory→⑤Action
4A Customer Journey
①Awareness→②Attitude→③Act→④Act again
Models that take into account online sharing and diffusion
5A Customer Journey
①Aware-②Appeal-③Ask-④Act-⑤Advocate
The customer journey has evolved over time from an era when it was considered a one-way to a form that reflects the customer’s online connected status. Let’s take a closer look at the customer journey in the 5A era.
What is Age of Connectivity in Kotler’s Marketing 4.0?
How the 5A customer journey has changed

The customer journey up to 4A is now redefined to accommodate the changes created by connectivity. In other words, it reflected the impact caused by the Internet-connected age.
In 4A, the individual customer determined his or her attitude toward the brand, but in 5A, the customer is now connected to the Internet, and the appeal of the brand is influenced by the community surrounding the customer, which is the final attitudinal decision of the customer.
In the world of 5A, many of the decisions which look personal to the customers are effectively social decisions in fact. The new 5A customer journey is a reflection of the impact caused by the Internet.
Processes and customer touch points of AWARE、APPEAL、ASK、ACT、ADVOCATE
The 5A customer journey reflects the connectivity among customers and is described as a process of 1) Aware, 2) Appeal, 3) Ask, 4) Act, and 5) Advocate. Let us examine these in detail.
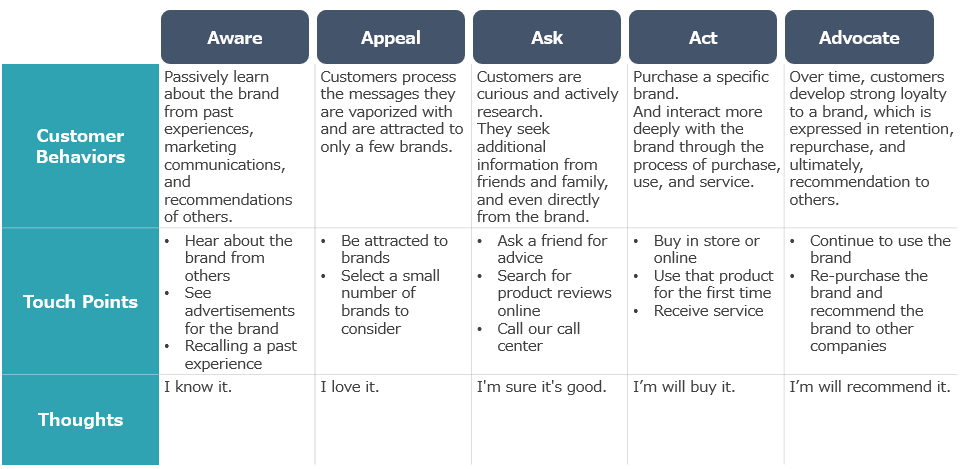
Edited by 5ALS Office, from figure 5-2 in Marketing 4.0
①AWARE is the traditional entry point to the customer journey. (Aware)ness is gained by being told by others or by viewing a brand’s advertisements.
②APPEAL is a state in which customers are attracted to only a few of the recognized brands that are desirable to them.
③in the ASK phase, customers research the brands they are attracted to. If they obtain detailed information during this ask phase, they may proceed to (4) action, or they may proceed to (5) advocate even if no purchase action is involved.
④ACT is not only purchasing behavior but also consumption and use, as well as communication through after-sales service.
⑤ADVOCATE is the stage where customers develop a strong loyalty to a brand and enthusiastic recommenders become evangelists, spontaneously recommending their favorite brands to others.
How has the customer journey changed with Marketing 4.0 4A to 5A?
5A customer journey, to aim all people who are aware of the brand will advocate it.
As mentioned in the previous section, the customer journey, which used to be funnel-shaped, is not squeezed in a straight line from left to right, from aware to advocate in 5A.
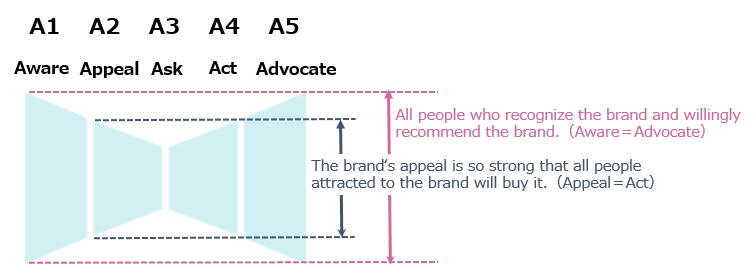
Customers are constantly connected to the Internet to obtain information from the online community or to recommend their favorite brands, and they are influenced by the actions of others and may suddenly be inspired by a recommendation from a friend to purchase the brand. There are also customer journeys that customers suddenly act upon without the steps from aware and appeal to ask.
Also, in categories where products are rare and popular, the 5A customer journey generates customers who advocate the brand even if they are not actual buyers, and customers can participate in the customer journey at any stage.
In traditional thinking, loyalty has been expressed in terms of customer retention and repurchase rates, but in the 5A customer journey, loyalty is expressed as the willingness to advocate a brand. The ideal model would be a situation in which (1) all people who are aware of the brand voluntarily recommend it (aware = advocate), and (2) all people who are attracted to the brand due to its extremely strong appeal purchase it (appeal = action) along the ideal state of the 5A customer journey. At this point, the customer does not feel the need to do the research themselves, and the volume of ask is at its lowest, so the shape of the 5A customer journey is bow-tie shaped.

